
The European livestock industry has been experiencing significant transformation, with a growing emphasis on enhancing animal performance and optimizing feed efficiency. At the center of this evolution is the rumen bypass fat (RBF) market, a specialized segment of animal nutrition designed to improve the energy intake of ruminants without negatively impacting rumen fermentation. Europe, with its strong dairy and livestock sectors, has emerged as a critical market for RBF, fueled by increasing demand for high-quality milk, meat, and sustainable farming practices.
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/europe-rumen-bypass-fat-market
Understanding Rumen Bypass Fat
Rumen bypass fat, also known as protected fat or bypass fat, is a type of dietary fat that bypasses the rumen and is digested in the small intestine. Traditional fats in animal feed often interfere with rumen microbial activity, reducing fiber digestion and overall feed efficiency. RBF, however, is designed to resist breakdown in the rumen while providing a concentrated energy source downstream in the digestive tract. This ensures that livestock receives the necessary energy for growth, lactation, and reproduction without compromising rumen health.
RBF plays a crucial role in meeting the nutritional demands of high-yield dairy cows and rapidly growing meat animals. Its adoption is closely linked to the rising need for feed strategies that enhance milk fat content, improve body condition scores, and reduce metabolic disorders.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Rising Dairy Production: Europe is home to some of the largest dairy-producing countries in the world, including Germany, France, and the Netherlands. The push for higher milk yield and improved milk quality drives the demand for nutritional solutions like RBF, which can enhance energy intake without disrupting rumen fermentation.
Focus on Animal Health and Productivity: Modern livestock farming emphasizes preventive nutrition to minimize metabolic issues such as ketosis, fatty liver syndrome, and poor fertility. RBF contributes to these goals by supplying concentrated energy that supports both production and health.
Feed Efficiency and Sustainability: With increasing feed costs and growing attention to sustainability, farmers are seeking solutions that maximize nutrient utilization. RBF allows animals to extract more energy from the same feed, reducing overall feed consumption and minimizing environmental impact through lower methane emissions and improved nutrient efficiency.
Technological Advancements: Continuous innovation in the production of RBF, including the development of different types of rumen-protected fats (e.g., calcium salts, encapsulated fats), has expanded its applicability and effectiveness in various ruminant diets.
Challenges
High Cost: Compared to conventional feed ingredients, RBF is relatively expensive, which can deter small-scale farmers from adopting it.
Regulatory Landscape: European regulations surrounding feed additives and animal nutrition are stringent. Manufacturers must comply with safety and quality standards, which may slow down product introduction and increase costs.
Lack of Awareness: Some farmers remain unaware of the benefits of RBF or may not have access to reliable guidance on optimal inclusion rates, limiting its market penetration in certain regions.
Opportunities
Expansion in Emerging Livestock Sectors: Beyond dairy, the growing meat production sector in Europe, particularly in countries focusing on beef and lamb production, presents an opportunity for RBF adoption to enhance growth rates and meat quality.
Integration with Precision Feeding: As precision livestock farming gains traction, RBF can be integrated into individualized feeding programs to optimize nutrient intake and animal performance.
Sustainable Production Practices: With sustainability becoming a major driver in European agriculture, RBF’s role in reducing feed inefficiency and lowering greenhouse gas emissions positions it as a favorable choice for environmentally conscious farmers.
Market Segmentation
The Europe Rumen Bypass Fat market can be segmented based on type, application, and form:
By Type:
Calcium salts of fatty acids
Encapsulated fats
Other rumen-protected fats
Calcium salts are among the most commonly used forms due to their stability in the rumen and effectiveness in delivering energy.
By Application:
Dairy cattle
Beef cattle
Sheep and goats
Dairy cattle dominate the market due to their high energy requirements for milk production. Beef cattle and small ruminants are emerging segments driven by intensive meat production.
By Form:
Powder
Granules
Pellets
Pelleted and granulated forms are preferred for ease of mixing with other feed components, whereas powders are often used in specialized feeding programs.
Regional Insights
Within Europe, certain countries drive the demand for RBF due to their large-scale livestock operations and progressive farming practices:
Germany: Known for its high-efficiency dairy farms, Germany is a leading market for RBF, driven by demand for premium milk and dairy products.
France: With a strong focus on both dairy and beef production, RBF is increasingly used to improve feed efficiency and animal health.
Netherlands: Innovative livestock management and precision feeding techniques make the Netherlands a key adopter of advanced feed solutions, including RBF.
Italy and Spain: These countries are experiencing moderate growth due to rising awareness and the adoption of intensive farming methods.
Eastern European countries are gradually emerging as markets for RBF as dairy and beef production modernizes and seeks higher efficiency.
Competitive Landscape
The European RBF market is moderately competitive, with a mix of established feed additive companies and smaller specialized manufacturers. Key players focus on product innovation, quality, and compliance with European feed regulations. Strategic partnerships with dairy cooperatives and feed distributors also play a critical role in market expansion.
Companies are increasingly emphasizing research and development to create RBF products tailored to specific animal needs, such as high-yield dairy cows or fast-growing beef cattle. Marketing strategies often highlight improved production performance, animal health benefits, and sustainability, aligning with the priorities of European livestock farmers.
Future Outlook
The Europe Rumen Bypass Fat market is poised for steady growth over the next decade. Several factors will contribute to this trajectory:
Increased Investment in Livestock Nutrition: Farmers are expected to invest more in advanced feed solutions to meet rising production targets and consumer demand for high-quality dairy and meat products.
Technological Integration: Smart feeding systems and precision nutrition will enable more targeted use of RBF, enhancing its effectiveness and adoption.
Sustainability Focus: As European agriculture increasingly emphasizes environmental responsibility, RBF’s role in reducing feed inefficiency and methane emissions will be more significant.
Regulatory Support for Safe Feed Additives: Continued support for scientifically backed feed solutions will encourage the use of RBF under strict safety and quality standards.
Conclusion
The Europe Rumen Bypass Fat market represents a critical segment of animal nutrition, supporting the region’s livestock sector in achieving higher productivity, improved health, and sustainable farming practices. Driven by technological innovations, the rising demand for quality milk and meat, and an increasing focus on feed efficiency, the market is set to expand steadily. While cost and regulatory challenges remain, opportunities in precision feeding, emerging livestock sectors, and sustainability initiatives present a promising outlook for manufacturers, farmers, and stakeholders in the European animal nutrition landscape. RBF is not just a feed additive; it is a strategic tool that empowers livestock farmers to meet the evolving demands of modern agriculture efficiently and sustainably.






 komal007
komal007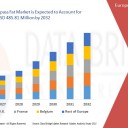
 ravindrankhx
ravindrankhx Erica111
Erica111 beckylh
beckylh